Changzhou Veidt Weighing Co., Ltd. © 2022 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Privacy Policy
Product Category
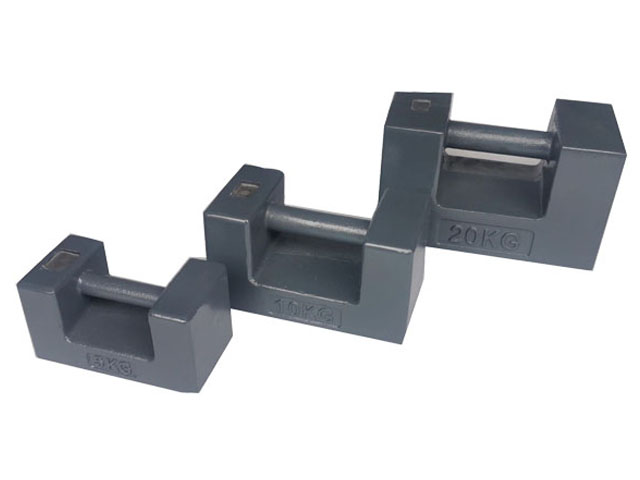
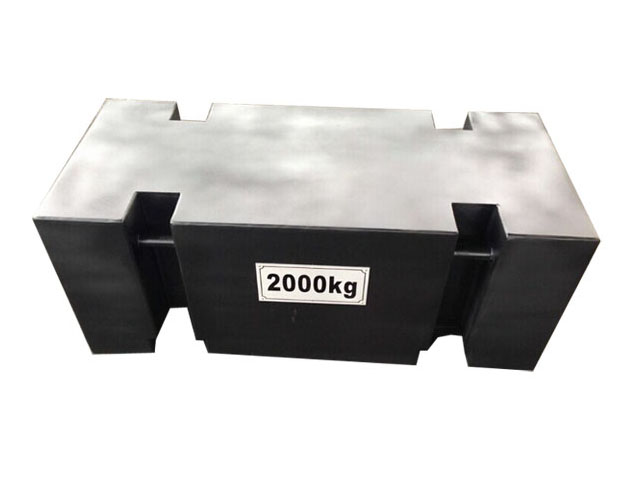
Test Weights
Veidt Weighing is a test weight factory in china, test weights are essential basic tools in the field of metrology, used for calibrating, testing, and verifying the accuracy of various weighing equipment. These precision manufactured metal blocks represent known and precise quality values, playing a critical role in laboratories, industrial production, and commercial transactions.
Classification of test weights
Test weights can be classified into various types based on their accuracy level and usage scenarios:
Classified by accuracy level
- E1 level weight: the highest precision level, used for calibrating high-precision balances and serving as a national metrology standard
- E2 level weight: laboratory grade high-precision weight
- F1 grade weight: precision industrial weight
- F2 grade weight: for general industrial use
- M1 level weights: suitable for commercial and industrial use
- M2 level weight: rough weighing purpose
Classified by material
- Stainless steel weights: the most common, highly corrosion-resistant, suitable for most environments
- Cast iron weights: Low cost, commonly used in industrial weighing systems
- Brass weights: Traditional material with certain oxidation resistance
- Aluminum alloy weights: lightweight, suitable for large and portable use
Technical characteristics of test weights
- Manufacturing standards
Modern test weights are manufactured strictly in accordance with the R111 recommendations or ASTM standards of the International Organization for Legal Metrology, ensuring consistency and reliability worldwide. - Surface treatment
High precision weights are usually subjected to special polishing treatment, resulting in extremely low surface roughness and reducing the effects of air buoyancy and static electricity. Some weights are treated with matte finish to reduce reflective interference. - Magnetic properties
High quality weights are made of materials with low magnetic susceptibility, usually less than 0.01, to avoid the influence of magnetic field on the weighing results.
Application areas of test weights
- Laboratory calibration: used for calibrating high-precision weighing equipment such as analytical scales and precision scales
- Industrial quality control: Regularly verify the accuracy of the weighing system on the production line
- Metrological verification: Government metrology departments conduct mandatory and arbitration verification
- Educational research: teaching physics experiments and quality measurement
- Commercial trade: Verify the accuracy of commercial scales to ensure fair transactions
Use and maintenance of test weights
Correct usage method
- Use specialized tweezers or gloves to handle and avoid direct contact with hands
- Handle with care to prevent collisions and scratches
- Before use, the temperature should be stabilized in the weighing environment
- Regular cleaning to remove surface dust and pollutants
Key points of maintenance and upkeep
- Store in a dry and dust-free environment
- Avoid contact with corrosive substances
- Regular inspection to ensure accurate measurement values
- Separate storage of weights of different grades to prevent confusion
Precautions for selecting test weights
- Select the appropriate accuracy level based on usage requirements
- Confirm the certification and traceability of weights
- Consider the temperature and humidity conditions of the usage environment
- Evaluate the technical support and service capabilities of suppliers
- Check the surface quality and machining accuracy of the weights
As the foundation of the measurement system, the quality of test weights directly affects the reliability of various weighing results. Whether it's precision experiments in scientific research institutions or daily weighing in supermarkets, these seemingly simple yet crucial metal blocks are indispensable. Correctly selecting, using, and maintaining test weights is the first step in ensuring measurement accuracy.